Accounting Standard
Introduction
Accounting standards are authoritative standards for financial reporting and are the primary source of generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). Accounting standards specify how transactions and other events are to be recognized, measured, presented and disclosed in financial statements. The objective of such standards is to provide financial information to investors, lenders, creditors, contributors and others that is useful in making decisions about providing resources to the entity.
In Malaysia, the accounting standards are issued by Malaysian Accounting Standards Board (MASB). It is established under Financial Reporting Act 1997 as an independent authority to develop and issue accounting and financial reporting standards in Malaysia.
There are two standards that you can apply in Malaysia:

MASB Approved Accounting Standards for Entities Other than Private Entities
 MASB Approved Accounting Standards for Private Entities
MASB Approved Accounting Standards for Private Entities
Which Accounting Standard I Shall Use?
The decision tree below helps an entity to decide which accounting framework should be used for its preparation of financial statements.
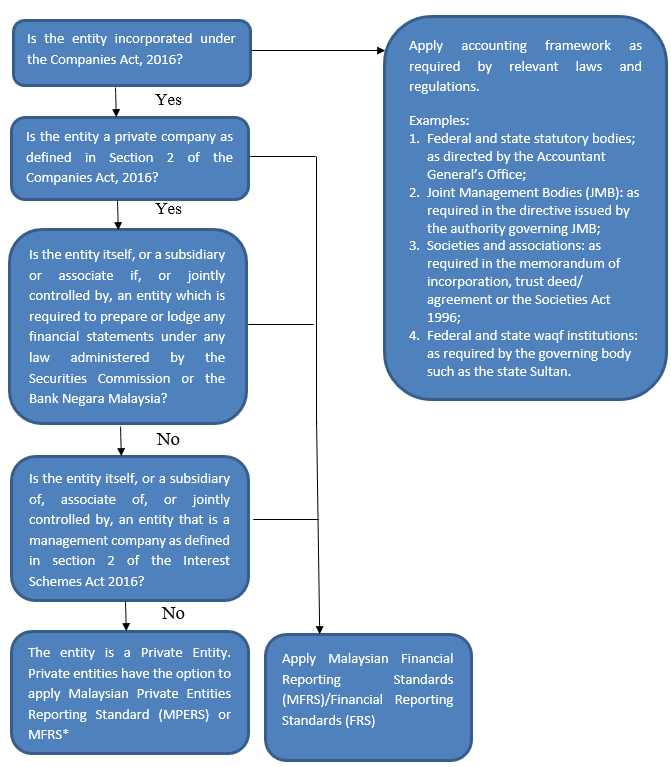
* Private entities that have applied FRSs shall apply either MFRS or the MPERS for annual periods beginning on or after 1 January 2018.
Definition of a Private Entity
The decision tree below helps an entity to decide which accounting framework should be used for its preparation of financial statements.
A private entity is a private company incorporated under the Companies Act 1965 that –
- is not itself required to prepare or lodge any financial statements under any law administered by the Securities Commission or Bank Negara Malaysia; and
- is not a subsidiary or associate of, or jointly controlled by, an entity which is required to prepare or lodge any financial statements under any law administered by the Securities Commission or Bank Negara Malaysia.
On 28 February 2017, the MASB had revised the Private Entity definition with the coming into operation of the Companies Act 2016 and Interest Schemes Act 2016, both on 31 January 2017. The revised definition is as follows and shall be applied for financial statements with annual periods ending on or after 31 January 2017:
A private entity is a private company as defined in section 2 of the Companies Act 2016 that –
- is not itself required to prepare or lodge any financial statements under any law administered by the Securities Commission or Bank Negara Malaysia; and
- is not a subsidiary or associate of, or jointly controlled by, an entity which is required to prepare or lodge any financial statements under any law administered by the Securities Commission or Bank Negara Malaysia.
Notwithstanding the above, a private company that is itself, or is a subsidiary or associate of, or jointly controlled by, an entity that is a management company as defined in section 2 of the Interest Schemes Act 2016 is not a private entity.
An entity may only be treated as a private entity in relation to such annual periods or annual periods throughout which it is a private entity.


 (201706002678 & AF 002133)
(201706002678 & AF 002133)